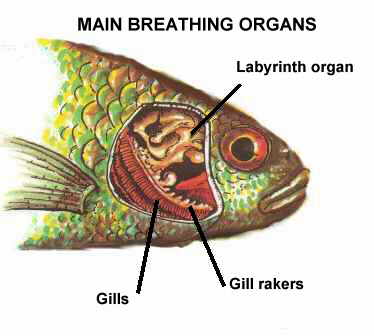
A certain group of fishes including Bettas, found in Asia and Africa, can breathe directly from the air, using a specialized organ called the labyrinth. The labyrinth organ is located inside the head just behind the gills. It has evolved to take oxygen directly from air additional to extracting it from the water.
Betta fishes, in their natural habitat, live in dirty, less oxygenated waters full of different creatures. These fishes tend to have enlarged fins and widebodies. The physical shape of the organ gives its name “labyrinth”, which literally means “maze.” The labyrinth contains plates that have thousands of oxygen-absorbing blood vessels, which gather air that is inhaled. The inhaled air is then trapped inside a group of folds and is eventually absorbed into the main bloodstream.
Better Swimming Space, Better Breathing.
Betta fishes can survive in a smaller aquarium space than that which is normally provided because they can extract oxygen from the air. However, this does not mean that Bettas can or should be kept in very crowded conditions or extremely tiny tanks. Even though they have the ability to breathe “extra” air, betta fishes still add as much waste to the water as their tankmates and need proper space and filtration for a healthy lifestyle. You will often see betta fishes for sale in small jars. The reason many dealers do this is to keep the males separated so that they don’t fight. This is not a good practice for the home aquarists to pick up and use. Don’t keep labyrinth fish in small bowls or hanging vases for decoration purposes. Provide them a nice healthy aquarium environment with plenty of room instead.

You need to provide heating, filtration and standard conditions to Labyrinth fishes just like any other need for a tropical fish.
Bettas, just like other tropical fishes, are vulnerable to diseases because of crowded tanks and poor water conditions. Take our word for it, they’ll be healthier and happier in a proper aquarium.